First, gas adsorption method
1. Test principle: The pore volume is obtained according to low temperature nitrogen adsorption, thereby obtaining porosity. This method can only obtain the pore volume of the pore structure of the size below 200 nm, and can not characterize the pores above 200 nm, which is not applicable to a large number of membranes.
2. Aperture test range: 0.35-500nm
3. Test membrane material pore size defects: test pore size range of 0.35-500nm; for micron-scale pores can not be tested; the pore throat diameter of the membrane material (ie the diameter of the narrowest hole of the through hole) is the most critical, the most important The nitrogen adsorption test does not distinguish between through holes and blind holes, so the aperture test error will be large.
4. Method test schematic:
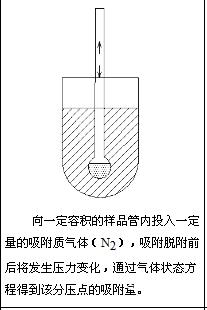
Second, the mercury intrusion method
1. Test principle: With the external force, the mercury is pressed into the dry porous sample, the volume of mercury in the sample is measured as a function of pressure, and the pore size distribution of the sample is calculated accordingly. This method also converts the non-breathable U-shaped holes, so the reference value of the measurement results is not large. If you want to test a small pore size, such as 100nm or less, you need a very large pressure (20MPa or more) to inject mercury into the pores of the material. This large pressure is absorbed by the general material. Under high pressure, the pore structure of the membrane material will be deformed or even Pressure, causing the result to deviate from the theoretical value;
2. Aperture test range: 50nm-500um
3. Test membrane material pore defects: (1) pore size range: 50nm-500um; if you want to test a smaller pore size, such as 100nm or less, you need a very large pressure (20MPa or more) to inject mercury into the material pores, such a large pressure It is generally unacceptable for organic materials. Under high pressure, the pore structure of the membrane material will be deformed or even collapsed, causing the results to deviate from the theoretical value; however, for the bubble pressure method, the pressure applied to the material is much smaller; (3) the same nitrogen Like adsorption, mercury intrusion cannot distinguish between through and blind holes, and it is impossible to characterize the size of the throat.
4. Test schematic
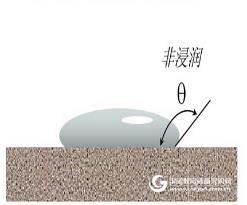

The liquid mercury between the particles is pressed into the pores, and the pore size invaded by the mercury is a function of the pressure used; the sample tube on the right shows the mercury injection/evaporation volume measurement through the metal jacket and the electrode cap (plate electrode).
Three, bubble point method
Test principle: When the channel is blocked by liquid wetting agent, due to the surface tension of the wetting agent, if the hole is opened by gas at this time, it is necessary to apply a certain pressure to the gas, and the smaller the hole, the hole is opened. The greater the pressure. By comparing the relationship between the pressure and the gas flow rate of the porous material in the dry and wet state, the pore size distribution of the sample can be obtained by calculation according to a certain mathematical model.
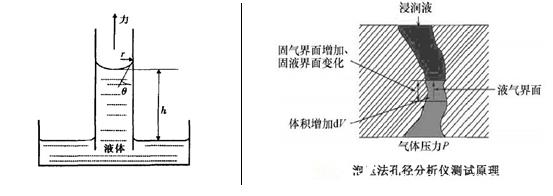
2. Aperture test range: 20nm-500um
3. For the gas-liquid discharge method, since the gas-liquid interface tension is large, the smaller pore diameter can only be measured by increasing the gas pressure, but the high pressure is liable to cause a series of problems such as gas leakage, sample deformation, and pressure drop. The drawback of the bubble point method is that it is not suitable for measuring membrane materials with small pore sizes.
4. Instrument test report screenshot
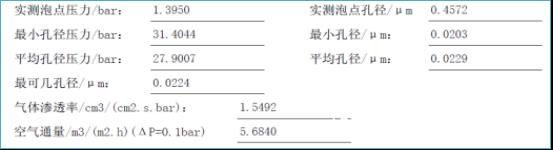
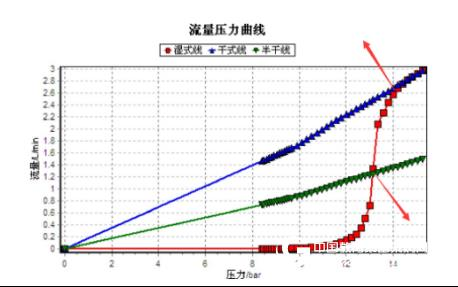
5. Instrument picture

Fourth, suspension filtration
1. Test principle: The spherical particle suspension is used as the medium, and the sample to be tested is used for cross-flow filtration. The pore size distribution can be calculated by comparing the particle size distribution of the original suspension and the permeate. The diameter of the particle is the maximum pore size of the porous material.
Five, liquid and liquid elimination method
1. The test principle is similar to the bubble point method, and is also used to measure the pore throat, except that another liquid that is incompatible with the wetting agent is used instead of the gas as the cell opener;
2. Test principle: 10nm-200um
3. Test membrane material pore size advantages and disadvantages: Because the liquid-liquid interface tension is small, only a small pressure is required to measure a large aperture, so the pressure measurement error is large, and the optimal measurement range is 10 nm to 200 μm.
Bubble pressure method (gas-liquid displacement) pressure-aperture correspondence
According to the formula: D = 4 γCos θ / ΔP, the calculation is as follows:
Pressure difference â–³P/bar
Aperture / μm
Infiltrate: water
γ=72.75mN/m
Infiltrate: poporil
γ=16mN/m
0.005
416.13
91.52
0.01
208.07
45.76
0.05
41.61
9.15
0.1
20.81
4.58
0.5
4.16
0.915
1
2.08
0.458
5
0.416
0.092
10
0.208
0.046
15
0.139
0.031
20
0.104
0.023
25
0.083
0.018
30
0.069
0.015
35
0.059
0.013
Red Light Therapy has been widely used in traditional clinical medicine, and the effect is remarkable. Medical-grade red light accelerates wound healing, reduces pain and inflammation, and stimulates collagen production anti aging. With the development of medicine and in-depth research, it has been proved that red light therapy in a specific band can be used to improve vision, and the color vision of the subjects improved by 20%.
Led Light Therapy Medical Device,Red Light Therapy Panel,Medical device for incresing collagen
Shenzhen Bonliter Optoelectronic Co., Ltd. , https://www.bonliters.com