When 3D printing is primarily used to produce models, prototypes, and disposable parts made from non-production-ready materials, there is no need for an enterprise-class solution like PLM. But as 3D printing goes into production, a series of advances from materials to machines and software make additive manufacturing a production process. To fully automate the quality control and process automation of additive manufacturing parts, this digital information must be integrated with the digital thread, and the importance of the product lifecycle management-PLM system is reflected.

Digital threads can be understood as a high-level description of PLM, which puts all digital information together (including files, metadata, document information, etc.), and the product lifecycle connects the entire process from idea to simulation, optimization and verification to 3D printing. , cooling and aftertreatment. James White, CIMdata's director of additive manufacturing practice, said: "Unfortunately, many companies in the additive manufacturing industry don't recognize this. Instead, they see the 3D printer as a separate production device. An isolated idea."
Few companies consider managing additive manufacturing data and its workflow through a PLM system. They did not realize that PLM is a business strategy, not a software tool, but designed for additive manufacturing (DFAM-design for additive manufacturing), which is also consistent with PLM.
At present, although many companies are advocating DFAM-designed for additive manufacturing, the idea of ​​leaving the PLM system is flawed because the combination of manpower, design, simulation and optimization, and production is not seamless, which leads to It is difficult for companies to judge whether a design is optimized.
Perhaps companies will think that PLM is suitable for traditional manufacturing, so it is not suitable for additive manufacturing. This ignores the nature of the PLM system. According to the definition of CIMDATA, PLM is applied between enterprises within a single location, within a company dispersed in multiple locations, and between companies with collaborative relationships in product development. A range of application solutions for the creation, management, distribution, and application of information throughout the lifecycle of a product that integrates product-related human resources, processes, applications, and information.
PLM exists in the lifecycle information of the management product. In this cycle, the existence of various means of production is allowed, including additive manufacturing techniques. This involves integrating the specific data requirements of the additive manufacturing process into the PLM management system. Standard processes such as PLM forms, search, workflow, bill of materials (BOM) are still valid, including with other applications (eg The integration of ERP and change management) is effective.
So how do you implement PLM to manage additive manufacturing parts and production processes? This requires understanding how additive manufacturing is a part of the PLM workflow, because the products manufactured by additive ultimately need to meet company standards such as cost, time, quality, inventory, unit number, etc., and this information must be clearly searchable and traceable. of. For example, if you need to provide a single 3D printed part for a car, airplane, or even an iPhone, if the part does not meet the standard, the entire product may be compromised. The PLM management system is an important link for 3D printing products to the supply chain system.
CIMdata has developed a four-tiered ladder to implement PLM for managing additive manufacturing parts and processes in the DFAM pyramid. The safety, traceability, repeatability and metrics data for additive manufacturing are the basis for supporting these four steps. On this basis, it is the four different levels of DfAM components, DfAM subsystem, DfAM working group and DfAM enterprise.
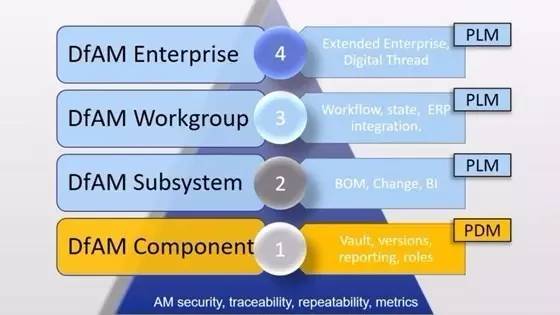
The following are the data management features required for each level, which illustrate the digital threads that connect all additive manufacturing information throughout the product lifecycle:
Pyramid layer requires data management
1 DFAM components: planning, data, methods and management, requiring PDM as a basic management tool
2 DFAM subsystem: BOM, change and business intelligence, requiring PLM as a management tool
3 DFAM Working Group: Workflow, Status, and ERP Integration, Requires PLM as a Management Tool
4 DFAM Enterprise: Extending enterprise and digital threads, requiring PLM as a management tool
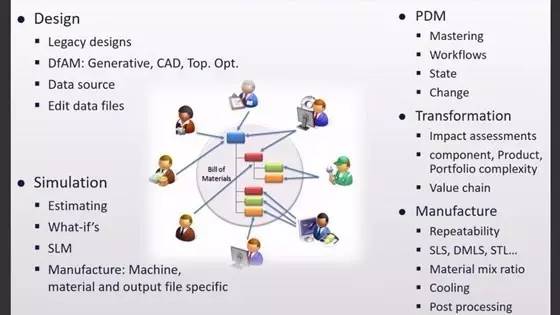
To implement DFAM, you must consider the additive manufacturing team (work activities that are tightly integrated with the machine) and their workflow (powder management, CAD / CAE, PDM, 3D printing, cooling, unpacking, and post-processing) and the business (all others) Sectors and tools outside the additive manufacturing working group involved).
In the enterprise, the additive manufacturing team may want them to have autonomy, just like a single production machine. In fact, when changes occur, every link in the product life cycle must share data and keep pace with each other. The interaction helps to reconcile the flexibility of the additive manufacturing work group.
(Editor)
Single Makeup Brush,Makeup Single Brush,Single Make Up Brush,Single Eyeshadow Brush
Guangzhou Yafei Makeup Toiletry Co.,Ltd , https://www.yfmakeupbrush.com