Wang Shouhong, a graduate of Wuhan Surveying and Mapping University in 1998, received a bachelor's degree in engineering from the Printing Department. He graduated from Wuhan University in 2001 with a master's degree in print and communication and is currently working at Guangdong Vocational College of Light Industry.
Energy curing ink concept
Various kinds of technologies in the printing industry emerge one after another, among which the fastest growing one is the energy curing technology. It means that the ink or coating material is fixed or hardened on the substrate under irradiation energy, so as to obtain a dry print. UV light and accelerated high energy electron beam (EB) are two energy forms of energy curing technology. Correspondingly, inks cured with UV light and EB energy, respectively, are called UV inks and EB inks.
Now, UV inks and EB inks are valued by many packaging and printing manufacturers, and their costs have been significantly reduced. UV inks and EB ink printing processes are increasingly worth studying.
Energy curing ink composition
The main chemical components of UV inks and EB inks include:
• Monomer (Reactive Diluent): A low molecular weight chemical that determines the surface properties of the ink after drying, such as gloss, hardening, and elasticity. Other monomers are the source of the harmful properties of energy-curable inks.
â— Resin (prepolymer): refers to the chemical skeleton of the ink, which will affect the ink's consistency, wetting ability and cross-linking properties.
â— Photoinitiator: A chemical substance that the ink becomes a high-energy state under the irradiation of UV light and begins to initiate the curing process. EB inks do not require a photoinitiator because the high energy electron beam has enough energy to initiate the polymerization reaction.
â— Additives: Including waxes, wetting agents, and ink transfer agents that change the properties of the ink, etc., which serve to specifically improve the physicochemical properties of the ink.
â— Pigment: The particle size and concentration of the colorant will affect the curing rate of the UV ink. Therefore, when choosing the color material, not only the color of the color material but also the wettability of the color material and the ability of receiving the UV light should be considered. Y and M inks are easier to cure, followed by C and K inks. This problem does not have to be taken into account when selecting pigments for EB inks, since the energy of high-energy electron beams is sufficient to cure thick ink film layers.
UV/EB ink curing principle
The drying of the ink film after the printing of common ink is that the binder (solvent, grease) in the ink is absorbed and volatilized by the substrate, and the solid material (color, resin, wax, desiccant, etc.) remains on the surface of the substrate. A thin layer of ink. General ink drying and energy curing ink fixation, the difference lies in the ink / coating coating chemical composition is different, followed by whether the printing shop needs to be equipped with energy curing device device.
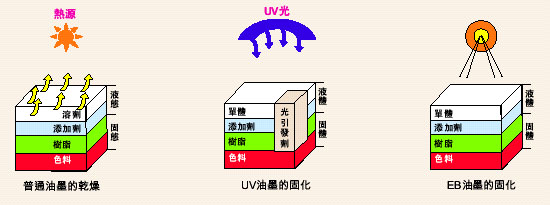
So called energy-curable inks, because they contain some chemical substances, they generate free radicals or ionic radicals under the action of UV light or high-energy electron beams, and radicals or ionic radicals are then cross-linked with other substances to form network polymers. . About the UV ink curing process, as shown below: 
Advantages and disadvantages of UV/EB inks
The first UV/EB ink cure time is very short, generally only 1/10 seconds can be completely dry and fixed on the substrate surface. For the traditional thermosetting ink and sheet-fed offset ink, the drying time may take several minutes. Even a few days can be completely dry, so the use of energy-curable ink printing offset printing jobs, delivery time is short, can be comparable with the flexo, gravure, and greatly enhance the offset printing production efficiency.
Secondly, after the UV ink is printed, it is processed by UV glazing, resulting in a high glossiness of the printed matter and a uniform and even surface. After the machine has been machined, the packaging and processing processes such as die cutting, creasing, gluing, and bronzing can be completed immediately.
The third print, printed with energy-curable ink, is very resistant. Due to the cross-linking reaction of the chemical substances in the ink, a macromolecular network polymer is formed, and the ink surface has strong chemical resistance and friction resistance.
The solid content of the fourth UV/EB ink after curing is close to 100%, and usually does not contain VOC (organic volatile matter). This strongly demonstrates that the UV/EB ink system is more environmentally friendly than the conventional ink system. If the chemical composition of UV/EB ink is appropriate, the odor of common inks dried by many oxidized conjunctivas is much smaller, and the printed surface is clean and free of dirt.
The fifth energy-curable ink is less and less irritating to human skin, and it is almost as irritating as ordinary ink containing a gasoline fraction.
Of course, energy-curable ink/glazing coatings also have some drawbacks. Some require either NBR or EPDM rollers. Offset printing may also require special blankets. The blankets may also require special cleaning agents to prevent the blankets from excessively shrinking, expanding, or reducing quality.
Second, it costs more than traditional inks. However, the high cost is worth compared to the final print performance.
In addition, a one-time investment in energy-curing equipment requires a certain amount of money. Current prices of UV curing equipment, UV lamps, and EB curing equipment have been steadily declining, and in particular, the price of EB curing equipment has dropped most significantly. Compared with ten years ago, the cost of EB curing equipment has been reduced by a factor of four. In the past few years, the price of UV-curing equipment has also been steadily declining. There are enough reasons to believe that the prices of energy-curing equipment will continue to decline in the next few years.
Latest Technical Progress of UV/EB Inks
Although there are some differences in performance between different manufacturers of mixed ink products, they should generally have the following characteristics:
â—Can be applied to all types of ordinary printing presses equipped with continuous curing unit
â—Need not to replace the various chemicals used in rubber rollers, blankets, printing plates or printing machines
â—Achieve higher print gloss in continuous printing processing
â—Use a conventional cleaning agent to clean the rubber roller, blanket, etc.
â— The printing processing adaptability on the printing press is comparable with the traditional grease type ink
Looking into the future of energy-curable inks in the printing industry, it is still dependent on whether the cost of ink can be reduced to that of ordinary inks.
Aluminum Strip,Aluminium Fin Strip,Aluminium Fin Strip for Radiators
Dafa Aluminum Industry Co., Ltd. , http://www.hnaluminiumfoil.com